Absolutely! Here’s a comprehensive 3000-word article about internet connection modalities, with “ tags replaced by `
` or `
` for a more structured, heading-based format:
The internet has become an indispensable part of modern life, facilitating communication, commerce, entertainment, and education. Understanding the various ways to connect to the internet is crucial for choosing the right option for your needs. This article explores the diverse range of internet connection modalities, detailing their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for different users.

From the dial-up era to the high-speed broadband of today, internet connection technologies have undergone a remarkable transformation. This evolution has been driven by increasing demand for faster speeds, greater reliability, and broader accessibility. Let’s delve into the different connection types that have shaped our digital landscape.
Wired connections, while often requiring physical infrastructure, generally offer greater stability and speed compared to wireless options.
Overview of DSL
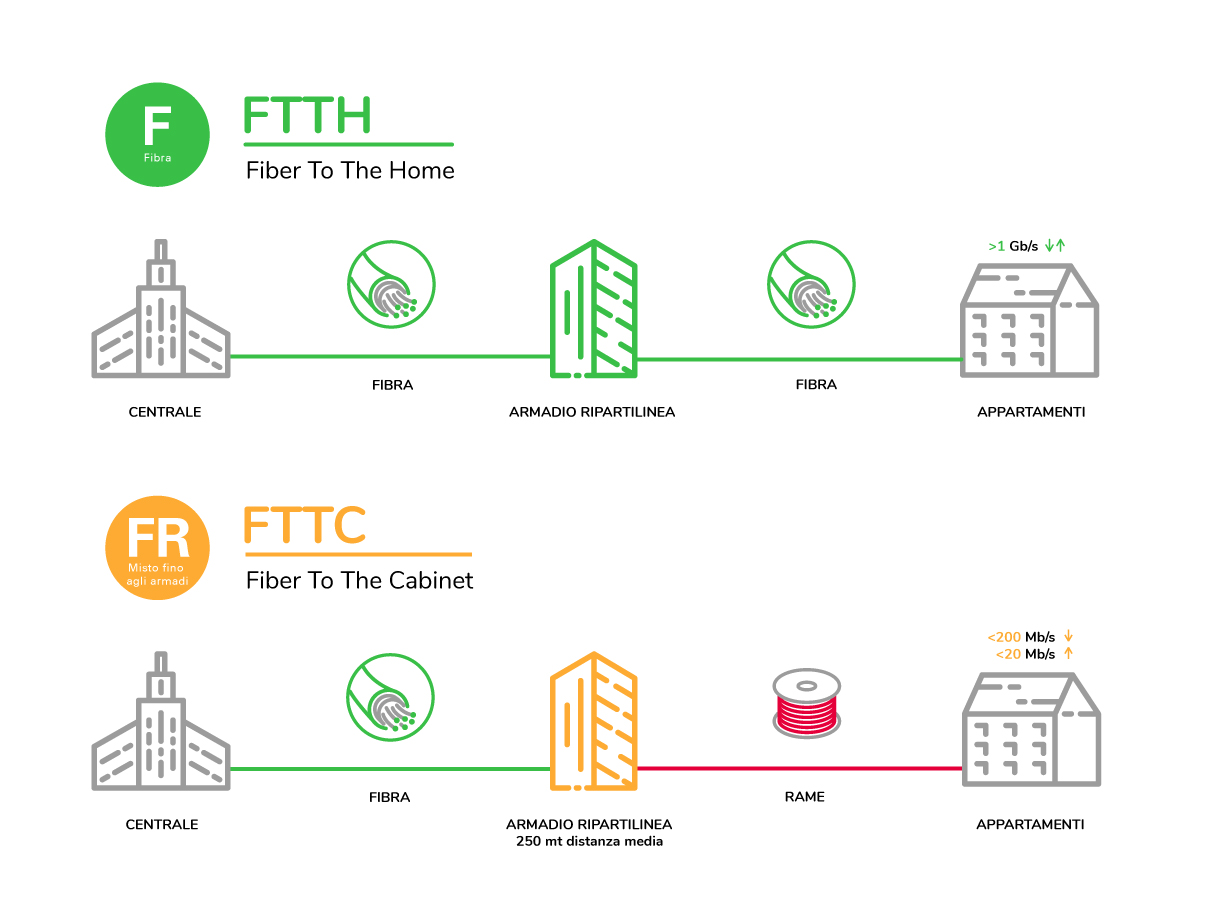
DSL technology utilizes existing telephone lines to transmit data, allowing simultaneous voice and internet usage. It comes in various forms, each with distinct characteristics.
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
ADSL provides faster download speeds than upload speeds, making it suitable for typical home internet usage, where downloading (e.g., streaming videos, browsing websites) is more frequent than uploading (e.g., sending large files).
Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL)
SDSL offers equal download and upload speeds, catering to businesses and users who require significant uploading capabilities, such as video conferencing or hosting servers.
Very-high-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL)
VDSL delivers much faster speeds than ADSL and SDSL, bridging the gap between DSL and fiber optic connections. However, its performance degrades over longer distances from the telephone exchange.
Advantages of DSL

Relatively widespread availability.
Disadvantages of DSL
Speed and performance can be affected by distance from the telephone exchange.
Overview of Cable Internet
Cable internet uses the same coaxial cables that deliver cable television services. It offers high-speed internet access through the cable television infrastructure.
Advantages of Cable Internet
High download speeds, often exceeding DSL.
Disadvantages of Cable Internet
Shared bandwidth can lead to slower speeds during peak usage times.
Overview of Fiber Optic Internet
Fiber optic internet transmits data through thin strands of glass or plastic, using light signals. It offers significantly faster speeds and greater bandwidth than DSL or cable internet.
Fiber to the Home (FTTH)
FTTH delivers fiber optic cables directly to individual homes, providing the highest possible speeds and reliability.
Fiber to the Premises (FTTP)
FTTP is a general term that includes FTTH, and also covers fiber connections to businesses and other locations.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Internet
Extremely high speeds and bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Internet
Limited availability, primarily in urban and some suburban areas.
Overview of Wired Ethernet
A direct wired Ethernet connection offers the most reliable connection. Primarily used in business settings, or for very stable home networks.
Advantages of Wired Ethernet
Very stable and reliable.
Disadvantages of Wired Ethernet
Requires physical cabling.
Wireless connections offer greater flexibility and mobility, but they can be more susceptible to interference and fluctuations in speed.
Overview of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly over short distances. It is the most common wireless internet connection for homes, offices, and public spaces.
Wi-Fi Standards
Various Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11ac, 802.11ax/Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, Wi-Fi 7) offer different speeds and capabilities. Newer standards provide faster speeds, greater capacity, and improved performance in congested environments.
Advantages of Wi-Fi
Convenient and flexible, allowing multiple devices to connect wirelessly.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi
Speed and performance can be affected by distance, interference, and congestion.
Overview of Mobile Broadband
Mobile broadband uses cellular networks (3G, 4G, 5G) to provide internet access to mobile devices.
3G, 4G, and 5G
3G networks provide basic internet access, while 4G LTE offers significantly faster speeds. 5G technology delivers even higher speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, enabling new applications and services.
Advantages of Mobile Broadband
Highly portable, allowing internet access from almost anywhere within cellular coverage.
Disadvantages of Mobile Broadband
Speed and performance can vary based on cellular signal strength and network congestion.
Overview of Satellite Internet
Satellite internet uses satellites in orbit to provide internet access to remote and rural areas where other connection options are limited.
Advantages of Satellite Internet
Available in remote and rural areas where other internet options are limited.
Disadvantages of Satellite Internet
High latency, due to the distance data must travel.
Selecting the appropriate internet connection modality depends on various factors, including:
Location: Availability of different connection types varies by location.
The landscape of internet connection modalities is diverse and constantly evolving. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option empowers users to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and circumstances. Whether you prioritize speed, reliability, or mobility, there is an internet connection modality that can meet your requirements. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and efficient ways to connect to the digital world.



